How Do Bacteria Reproduce Asexually
Bacteria Reproductive cells can multiply apace. Given the right weather condition, a single E. coli tin can grow into a billion-strong colony in simply a few hours.
Check out awesome, educational VR rooms on Inspirit'southward mobile app (available for iOS and Android devices)🤩
Introduction:
The fact that leaner are single-celled prokaryotic creatures prevents the existence of a male or female form of the organism. Bacteria reproduce asexually! When an asexual reproduction process is used, the 'parent' creates a genetically identical replica of themselves.
How do leaner reproduce?
Binary fission is the asexual reproduction method used past leaner, and it is the most mutual method.
- A single bacteria divides into two different cells, each unique.
- There are no differences between these cells or between them and their parent cells.
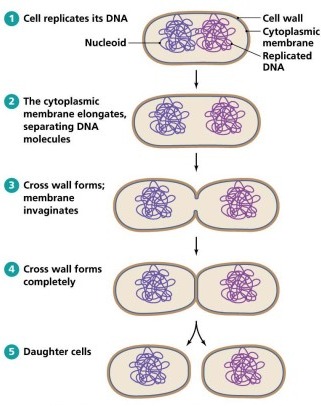
- The beginning of the fission process is marked by the replication of DNA in the parent bacterium. T
- here are 2 daughter cells formed as the cell becomes longer.
Temperature and the availability of nutrients affect reproduction in various ways, including the rate and timing of the procedure. East.coli, often known as Escherichia coli, produces roughly 2 meg germs every seven hours nether ideal circumstances. There are merely a few highly uncommon cases of sexual reproduction occurring during bacterial reproduction.
Bacteria tin undergo genetic recombination by conjugation, transformation, or transduction. As a result of the bacterium'due south genetic diversity, it may probable become antibiotic-resistant (as opposed to asexual reproduction where the aforementioned genetic textile is present in generations).
 Source
Source
Which of the following might or might not happen during Binary Fission?
Binary fission splits the chromosome into two identical copies, and the cell then divides into two new cells called 'daughters.' Each of the two daughters contains two exact copies of the mother jail cell. Binary fission may occur in a couple of milliseconds, and certain species of bacteria may triple their population in less than ten minutes! Bacteria colonies may be started with only one cell using this procedure.
Dna Recombination and Commutation
Is in that location a difference between male person and female bacteria? Of course, the answer is a resounding no. Equally a result, sexual reproduction is non possible in bacteria. Still, not all newly discovered bacteria are clones since bacteria may larn new DNA. There are three distinct methods in which this Bacterial Reproduction procedure takes identify:
Bacterial asexual reproduction
-
Binary fission – This is when a unmarried bacterial cell divides into two daughter cells. Initially, the bacterial cell reaches a threshold size and composition—replication of the bacteria's round double-stranded DNA results in the production of new complementary strands. Following the transfer of these ii Dna strands to the cell's opposing poles, a transverse septum develops in the jail cell's central region, dividing the two new daughter cells. Binary fission I have now been achieved. It is a straightforward technique that takes just a few minutes to complete.
-
Conidia creation - Conidia are generated past forming a transverse septum at the filament'south tip-in filamentous bacteria such as Streptomyces. The conidiophore is the office of the mother cell that carries the conidia; subsequently existence detached from the mother jail cell, it germinates on a suitable substrate, forming a new mycelium. Additionally, fragmentation is a term used to describe this kind of asexual reproduction.
-
Budding - During this reproduction stage, the bacterial cell develops a slight bulge on one side that continuously expands in size. Simultaneously, the nucleus separates into 2 halves, one of which includes some cytoplasm that enters the swelling, and the other remains fastened to the mother cell. The protrusion is referred to as a bud, and forth with the mother prison cell, it eventually forms a partition wall. This kind of reproduction is too known as vegetative reproduction in bacteria. Take, for example, Rhodomicrobium vannielii.
-
Cysts - Cysts are formed when additional layers form around the mother jail cell and act every bit a resting structure nether bad conditions. When the mother cell's surroundings improve again, she resumes her usual behavior, and Azotobacter is i such organism.
-
Endospore formation - Endospores are formed when a bacterial cell is stressed by desiccation or hunger. They consist of a central protoplast and a cadre containing DNA, ribosomes, enzymes, and t-RNA necessary to create a new cell. Only one endospore is formed in a single bacterial cell, and upon formation, it generates a new bacterial cell.
Sexual reproduction - Leaner
- Conjunction: Conjunction is the process by which Deoxyribonucleic acid passes via an extension on the surface of one leaner and travels to the surface of another bacterium (Figure below). Bacteria must substitution Dna with one some other to survive.
- Transformation: Bacterial transformation occurs when leaner take up fragments of DNA from their surrounding surround.
- Transduction: This kind of sexual reproduction occurs when a virus introduces strange genes into the bacterial jail cell. These viruses, dubbed bacteriophage, are non-pathogenic, and the virus acts every bit a carrier of genes from one host to another. When transducing bacteriophages include identical genes, the replication mechanism is restricted transduction. Additionally, they may communicate a large number of genes over some time. A procedure called generalized transduction.
Conclusion:
- Microorganisms reproduce via binary fission, which results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
- Reproduction In Bacteria can exchange DNA via the conjugation, transformation, and transduction mechanisms, among others.
FAQs:
1. What are the 3 ways bacteria reproduce?
Bacterial sexual reproduction may take place in 3 different ways:
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Conjugation
ii. How do bacteria reproduce sexually?
Only bacteria and archaea reproduce primarily by binary fission. Leaner are sexually unable, although they are capable of transferring genetic information. 2 bacteria come into contact through a hair and exchange genetic cloth (a bacterial structure). This is known as conjugation.
3. Do all leaner reproduce sexually or asexually?
Even though bacteria are single-celled prokaryotic creatures, they do not take a male or female counterpart. Bacteria reproduce asexually.
4. What are the ii methods of bacterial reproduction?
- Microorganisms reproduce by binary fission, producing two daughter cells identical to the parent cell.
- By using the mechanisms of conjugation, transformation, and transduction, bacteria may share DNA.
5. What blazon of asexual reproduction practise bacteria nearly commonly use?
Binary fission is a common and simple mechanism for asexual reproduction in bacteria. When asexual reproduction occurs, the nucleus of a parent prison cell divides in half, resulting in ii equal-sized girl cells.
6. Does E.coli reproduce sexually or asexually?
Escherichia coli splits, asexual reproduction occurs because genetic material is not transferred during cell division.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Leaner Reproduction! Bring together our Discord community to go any questions you may accept answered and to appoint with other students just similar you! Don't forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms - we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Reproduction and growthhttps://world wide web.britannica.com/science/microbiology/Reproduction-and-growth Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
- Leaner Reproduction
- https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-ii.0/section/vii.6/primary/lesson/prokaryote-reproduction-bio/ Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
- Bacteriahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacteria Accessed on seven Dec 2021
- Reproduction in Bacteriahttps://world wide web.vedantu.com/biology/reproduction-in-bacteria Accessed on 7 Dec 2021
How Do Bacteria Reproduce Asexually,
Source: https://www.inspiritvr.com/general-bio/prokaryotes-and-viruses/bacteria-reproduction-study-guide
Posted by: graydowits.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How Do Bacteria Reproduce Asexually"
Post a Comment