How To Calculate Osmotic Pressure
The minimum pressure required to prevent the inward menstruum of a solution'south pure solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known equally the osmotic pressure. It's too known as the osmosis index, which measures a solution's inclination for absorbing a pure solvent. The highest osmotic force per unit area that a solution could create if separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane is known every bit potential osmotic pressure.
When a selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs. From a low-concentration solution to a solution with a higher solute concentration, solvent molecules motion selectively through the membrane. Solvent molecules will continue to be transferred until equilibrium is reached.
Table of Contents
- What is Osmotic Pressure?
- What is Osmosis?
- Examples
- Summary
- Solved Exercises
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is Osmotic Pressure level?
Osmotic pressure tin can be divers every bit the minimum pressure level that must be applied to a solution to halt the menstruation of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Osmotic pressure tin can be calculated with the help of the post-obit formula:
π = iCRT
Where,
- π is the osmotic force per unit area
- i is the van't Hoff gene
- C is the molar concentration of the solute in the solution
- R is the universal gas constant
- T is the temperature
This human relationship between the osmotic pressure of a solution and the molar concentration of its solute was put forward by the Dutch chemist Jacobus van't Hoff. Information technology is important to note that this equation only holds true for solutions that bear similar ideal solutions.
Understanding Osmotic Pressure level – What is Osmosis?
The term 'osmosis' refers to the move of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region where the solute concentration is low to a region where the solute concentration is high. Eventually, an equilibrium is established between the ii sides of the semipermeable membrane (equal solute concentration on both sides of the semipermeable membrane).
Important note: The semipermeable membrane only allows the movement of solvent molecules through it – solute particles cannot pass through it.
If sufficient pressure is practical to the solution side of the semipermeable membrane, the process of osmosis is halted. The minimum amount of force per unit area required to nullify the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure level.
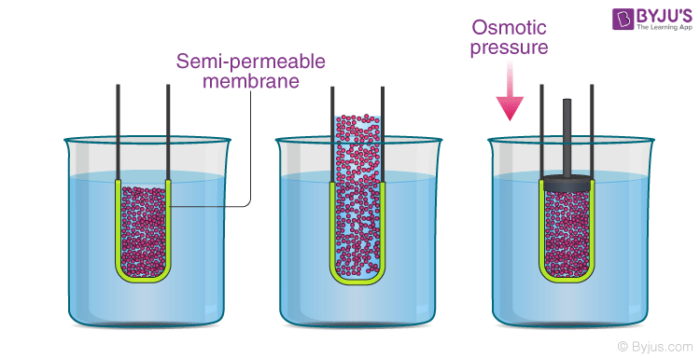
In the illustration provided above, information technology can be observed that the solvent molecules tend to laissez passer through the semipermeable membrane into the solution side until the osmotic force per unit area (of the solution) is applied to the solution side.
What happens when Force per unit area of Higher Magnitude than the Osmotic Pressure is Applied to the Solution Side?
In such a scenario, the solvent molecules would beginning moving through the semipermeable membrane from the solution side (where the solute concentration is high) to the solvent side (where the solute concentration is low). This process is called reverse osmosis (click the hyperlink to learn more virtually information technology!).
Examples and Applications
Plants maintain their upright shape with the assist of osmotic pressure. When sufficient water is supplied to the establish, its cells (which contain several salts) absorb water and expand. This expansion of plant cells increases the pressure level exerted on their cell walls, causing them to stand upright.
When insufficient h2o is supplied to the found, its cells go hypertonic (they shrink due to loss of h2o). This causes them to wilt and lose their house, upright posture. The measurement of osmotic force per unit area can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds.
Another important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater, which involves the process of reverse osmosis.
Summary
| What is osmosis? | The flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane. |
| What is a semipermeable membrane? | A membrane which just allows solvent molecules to flow through it. |
| What is the management of solvent flow? | From the solvent side to the solution side (from the region of low solute concentration to the region of high solute concentration). |
| What is osmotic force per unit area? | The pressure that must be applied to halt osmosis. |
| Where must the osmotic pressure level exist applied? | On the solution side of the semipermeable membrane (high solute concentration). |
| What is the formula for osmotic pressure level? | π = iCRT |
Solved Exercises
Exercise one
Ane mole of table common salt is dissolved in one litre of water. At a temperature of 27oC, what would be the osmotic temperature of this solution?
The molar concentration of table salt (sodium chloride) in the solution = 1mol/1litre = 1M
Since salt (NaCl) dissociates into two ions, the value of the van't Hoff gene hither is 2. Converting 27oC to the Kelvin scale, the required temperature becomes 300K.
Therefore, the osmotic pressure of the solution is:
π = (2) * (1 mol.L-one) * (0.0821 atm.50. mol-1.One thousand-ane) (300 K)
π = 49.26 atm.
The osmotic force per unit area of the 1M salt solution is 49.26 atmospheres at a temperature of 27oC.
Exercise ii
The osmotic pressure of a potassium chloride solution (at 300K) is 50 atmospheres. What is the tooth concentration of potassium chloride in this solution?
Rearranging the osmotic pressure equation, the following equation can be obtained:
π = iCRT ; C = π/(iRT)
Here, the value of i is 2 (since KCl dissociates into two ions). Therefore, the molarity of KCl is:
C = (50 atm)/(2)*(0.0821 atm.L.mol-1.One thousand-1)*(300K)
C = l/49.26 M = one.015 Chiliad
Therefore, the molar concentration of potassium chloride in the solution is 1.015 M.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What does osmotic pressure level depend on?
The temperature and the initial concentration of the solute affect osmotic pressure. Information technology is interesting to annotation that it is independent of what is dissolved. Two solutions of unlike solutes, such as alcohol and saccharide, will take the same osmotic pressure if their concentrations are the same.
What happens when food'south osmotic pressure level increases?
When a food'south osmotic pressure is increased by drying information technology or adding sugars or salts, the amount of water available to the bacterial prison cell is reduced. The efflux of water from microorganisms into the external environment is the most common response to an osmotic upshift.
Why does osmotic pressure depend on temperature?
The extra pressure that must exist practical to the solution's surface in order to prevent pure solvent osmosis. The osmotic pressure always increases as the temperature increases because of vant Hoff equation π = iCRT.
What is the difference betwixt Oncotic force per unit area and osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure level is the pressure level required to stop the net movement of water across a permeable membrane that divides the solvent and solution, whereas oncotic pressure is the contribution of colloids to total osmolality.
What happens when osmotic pressure and temperature are aforementioned?
When osmotic pressure level and temperature are both equal, an equivalent volume of solution contains a same number of moles of solute.
To acquire more about osmotic pressure and other colligative properties (such equally boiling indicate elevation), register with BYJU'S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
How To Calculate Osmotic Pressure,
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/osmotic-pressure-equation/
Posted by: graydowits.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Calculate Osmotic Pressure"
Post a Comment